Blood sugar 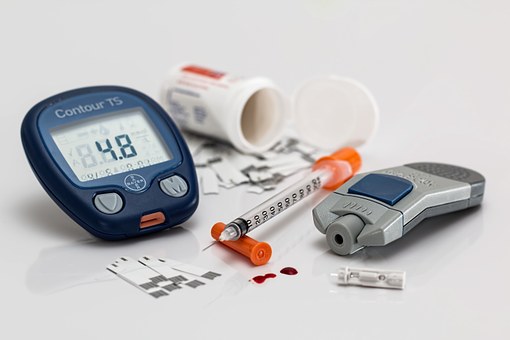
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is sugar that the blood carries to all the cells within the body to provide energy. Blood glucose or blood sugar measurements represent the quantity of sugar being transported in the blood throughout one instant. The sugar comes from the food we eat.
• Oral glucose tolerance test - This test is most typically performed throughout maternity. ...
• Fasting blood glucose. This is often a standard check because it is easy to perform. ...
• Two-hour postprandial test. ...
• Random blood glucose. ...
• Hemoglobin A1C check
Blood sugar fasting
If you had a fasting blood sugar test, that is between 70 and 100 mg/dl is normal. If you had a random glucose test, a standard result depends on when you last ate. Most of the time, the glucose level are below 125 mg/dl.
A fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dl is normal. A fasting blood glucose level from 100 to 125 mg/dl is taken into account pre-diabetes. If it's 126 mg/dl or higher on two separate tests, you've got diabetes.
Normal blood sugar levels
Normal blood glucose levels are less than 100 mg/dl after not intake (fasting) for a minimum of eight hours and they are less than 140 mg/dl 2 hours after eating. For many individuals without diabetes, blood glucose levels before meals hover around 70 to 80 mg/dl.
For the common person, it's 70 to 105 mg/dl in an exceedingly fasting state. (Diabetes is diagnosed once the abstinence glucose level is at or higher than 126 mg/dl.) Glucose values vary depending on the time of day, your activity level, and your diet.
Low blood sugar levels
Low blood glucose can happen in people with diabetes who take medications that increase insulin levels within the body. Taking an excessive amount of medication, skipping meals, eating less than normal, or workout more than usual can result in low blood glucose for these people. Blood sugar is also best-known as glucose.
Symptoms of high blood sugar levels
If your blood sugar level is too high, you may experience:
• Increased thirst.
• Frequent urination.
• Fatigue.
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Shortness of breath.
• Stomach pain.
• Fruity breath odor.
• A very dry mouth.
7 Foods That control blood glucose
• Raw, Cooked, or Roasted Vegetables. These add color, flavor, and texture to a meal. ...
• Greens. Go beyond your regular salad and try kale, spinach, and chard. ...
• Flavorful, Low-calorie Drinks. ...
• Melon or Berries. ...
• Whole-grain, Higher-fiber Foods. ...
• A very little Fat. ... Health is a blessing
• Protein.
Does sugar cause diabetes?
Sugar does not cause diabetes. However, there's a way that sugar can influence whether someone gets kind 2 diabetes. Consuming an excessive amount of sugar (or sweet foods and drinks) can make people put on weight.
Does meat cause diabetes?
Eating meat linked to a higher risk of diabetes. Higher intake of red meat and poultry is related to considerably raised the risk of developing diabetes, that is partially attributed to their higher content of heme iron in these meats, new research shows.
Does fat cause diabetes?
Having an excessive amount of saturated fat in your diet will cause high levels of what is referred to as 'bad cholesterol' (low-density lipoprotein or LDL), that will increase the danger of disorder (CVD). People with diabetes are at high risk of CVD, therefore it's even more important to form healthier food decisions.
What are the Treatments for Diabetes?
Diabetes may be a serious illness that you just cannot treat on your own. Your doctor can assist you to make a diabetes treatment plan that's right for you -- which you'll be able to understand. You may also want different health care professionals on your diabetes treatment team, as well as a specialist, dietitian, eye doctor, and a diabetes specialist (called an endocrinologist).
Treatment for diabetes needs keeping close check out your blood glucose levels (and keeping them at a goal set by your doctor) with a combination of medicines, exercise, and diet. By paying attention to what and after you eat, you'll be able to minimize or avoid the "seesaw effect" of quickly changing blood glucose levels, which might need fast changes in medication dosages, particularly insulin.
Tips to live a healthy life while having diabetes
1. Exercise regularly. Regular exercise will help you slim down and increase insulin sensitivity. ...
2. Control Your Carb Intake. ...
3. Increase Your Fiber Intake. ...
4. Drink Water and stay hydrated. ...
5. Implement Portion management. ...
6. Select Foods With a low Glycemic Index. ...
7. Control Stress Levels. ...




0 comments:
Post a Comment